|
This technique is especially useful if the surface tension of the melt is so low that the floating
zone would be unstable. The material to be melt should be electrically conductive, and its vapor pressure
negligible at the melting point.
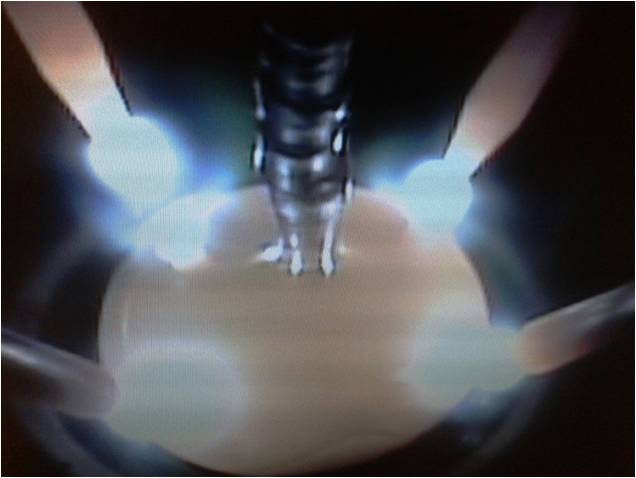
The melting takes place due to the heat of four electric arcs generated
between the melt surface and four tungsten electrodes. The top-seeded Czochralski growth is initiated by a matetrial
seed or a tungsten rod. A shallow water cooled copper crucible is used as a container for the melt and as a sink for
the charge and heat.
|
 |
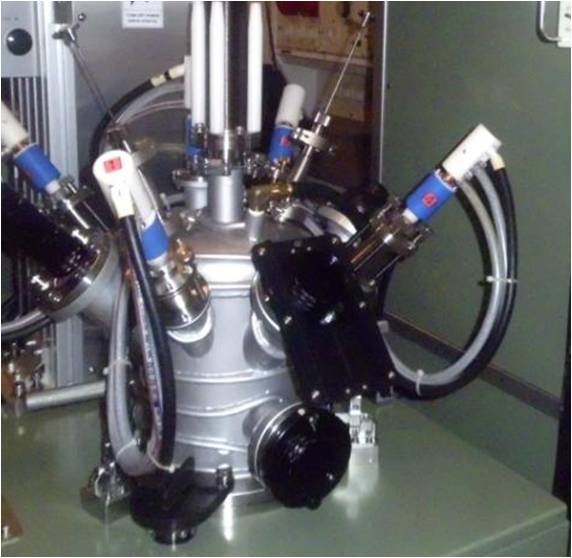 |
Melt heated by four arcs
and seeded by a W-rod
|





